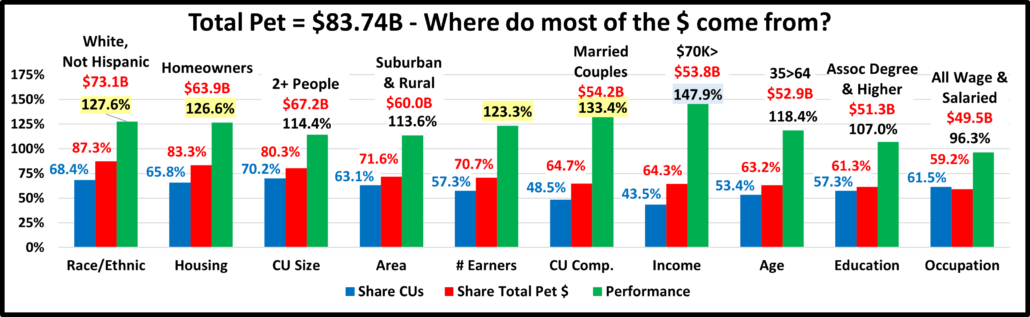
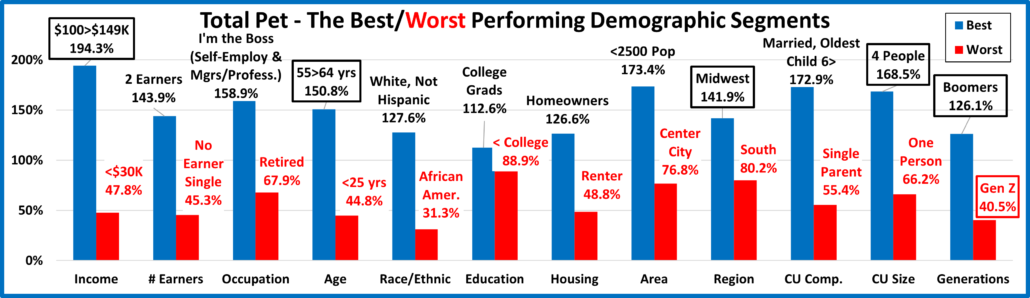
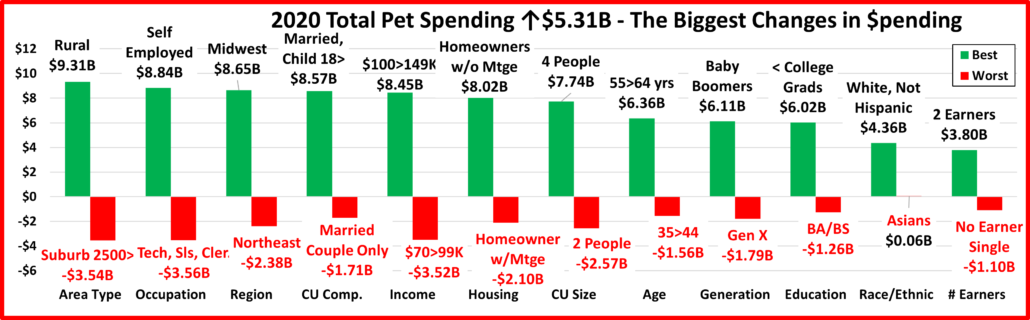
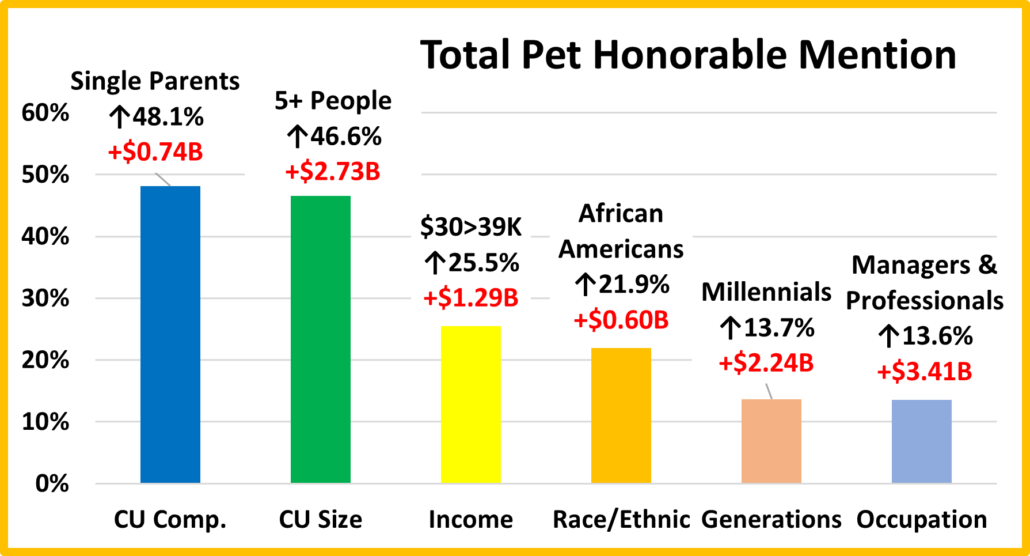
Petflation 2022 – April Update: +8.1%, 97.6% of National Inflation Rate
Inflation continues to make headlines. There have been year over year increases in the monthly Consumer Price Index (CPI) larger than we have seen in decades. In April the CPI was up 8.3% vs 2021, only down slightly from 8.5% in March. Food at Home (groceries) prices continue to surge, up 10.8% over 2021. March was +10%. These are the only double-digit YOY monthly percentage increases in this category since 1981. As we have seen in recent years, even minor price fluctuations can affect consumer pet spending, especially in the more discretionary pet segments. With that in mind, we will continue to publish monthly reports to track petflation as it evolves in the marketplace.
Total Pet prices were 4.1% higher in December 2021 than in December 2020, while the overall CPI was up 7.0%. In March 2022, Total Petflation was up +7.5% vs 2021 and the overall CPI was +8.5%. The gap significantly narrowed. In April, Petflation was 8.1%, 97.6% of the national rate of 8.3%. Now, the gap is virtually nonexistent. Let’s look a little deeper. This and future reports will include:
- A rolling 24 month tracking of the CPI for all pet segments and the national CPI. The base number will be pre-pandemic December 2019 in this and future reports, which will facilitate comparisons.
- Monthly comparisons of 22 vs 21 which will include Pet Segments and relevant Human spending categories. Plus
- CPI change from the previous month
- Inflation changes for recent years (20>21, 19>20, 18>19)
- Total Inflation for the current month in 2022 vs 2019
- Average annual Year Over Year inflation rate from 2019 to 2022
- YTD comparisons
- YTD numbers for the monthly comparisons #2>4 above
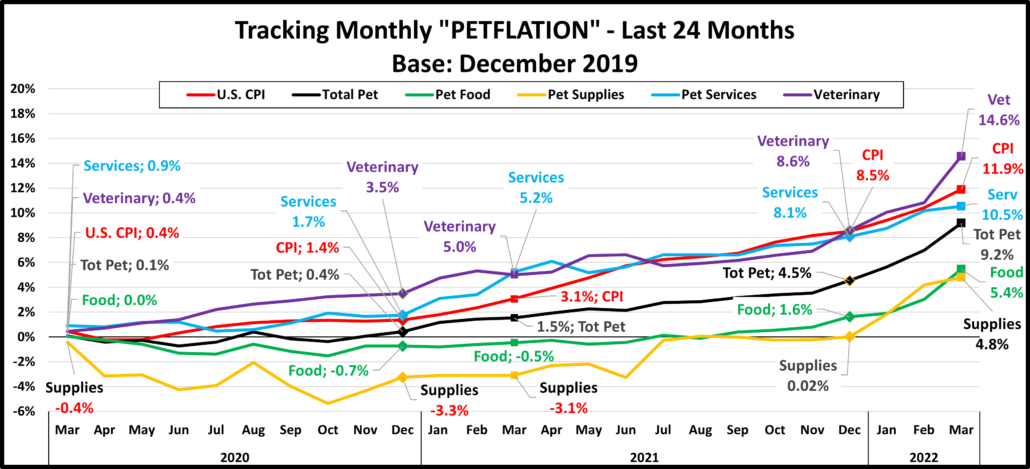
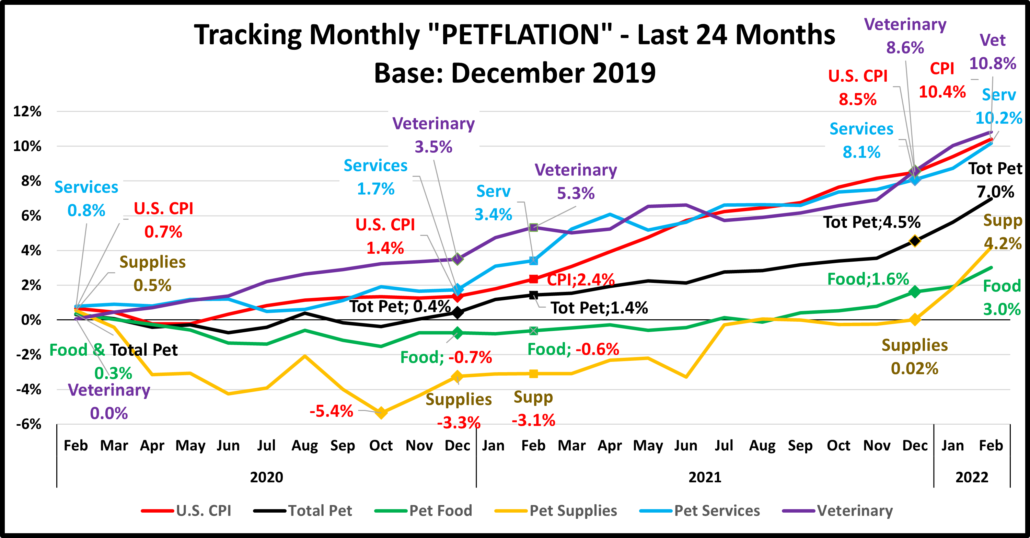
In our first graph we will track the monthly change in prices for the 24 months from April 2020 to April 2022. We will use December 2019 as a base number in this and future reports so we can track the progress from pre-pandemic times through an eventual recovery. Inflation is a complex issue. This chart is designed to give you a visual image of the flow of pricing. You can see the similarities and differences in patterns between segments and compare them to the overall U.S. CPI. The current numbers plus those from 12 and 24 months earlier are included as are the yr-end numbers for 2020 & 2021.This will give you some key waypoints for comparisons.
The pandemic began in March but hit home in April. Even the national CPI deflated, but not the Services segments. There are 2 different patterns between the Services and the Products segments. Veterinary and Services prices generally inflated after mid-2020, a pattern similar to the overall CPI. Food and Supplies prices generally deflated until late 2021. After that time, inflation took off. In March the rate of increase over the prior month slowed for Services and Supplies but accelerated for Food and Veterinary. In April, Supplies deflated but the others grew. Here are some things to note:
- U.S. CPI – The inflation rate was below 2% through 2020. It turned up in January 2021 and continued to grow through April 2022. 89% of the overall 12.5% increase since 2019 occurred in the last 16 months.
- Pet Food – Prices stayed generally below December 2019 levels from April 2020 to September 2021, when they turned up. There was a sharp increase in December. 88% of the 6.7% total has happened since November.
- Pet Supplies – Remember that Supplies prices were high in December 2019 due to the added tariffs. They had a “deflated” roller coaster ride until mid-2021 when they returned to December 2019 prices and essentially stayed there until 2022 when they turned sharply up reaching a new all-time pricing high in January, beating the 2009 record. They continued to set new price records in February and March, but prices turned down -0.1% in April.
- Pet Services – Normally inflation is 2+%. Perhaps due to closures, prices increased at a lower rate in 2020. In 2021 consumer demand increased but there were fewer outlets. Inflation grew in 2021 with the biggest lift coming in Jan>Apr. Inflation got even stronger in 2022, slowed a little in March, then turned up again in April
- Veterinary – Inflation has always been something that you can count on in Veterinary Services. Prices began moving up in March 2020 and grew consistently through the 2021 recovery. Then a pricing surge began in December which pushed them past the overall CPI with total inflation since 2019 reaching +15.5% in April.
- Total Pet – The blending of the segment patterns made the Pet Industry appear calm compared to the overall market. That ended in December 2021 as prices surged for all segments. In April inflation grew in all but Supplies.
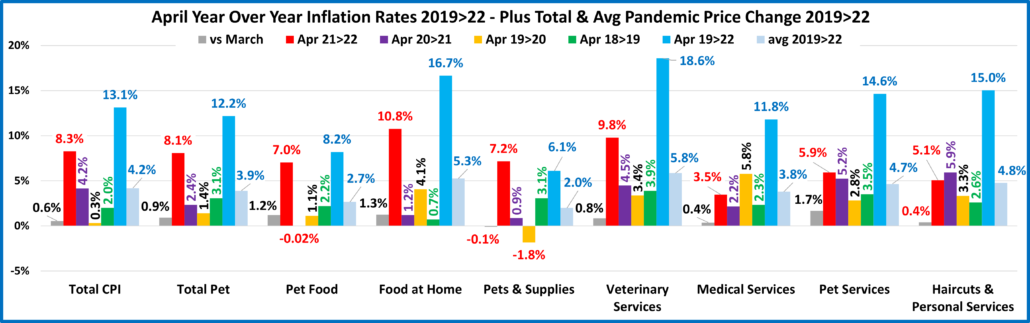
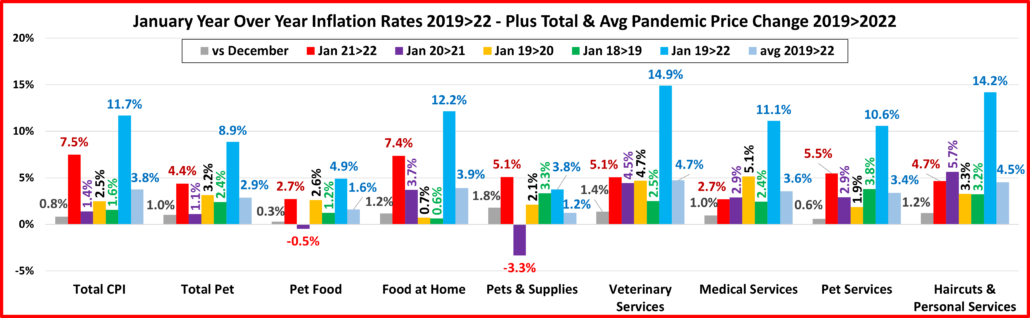
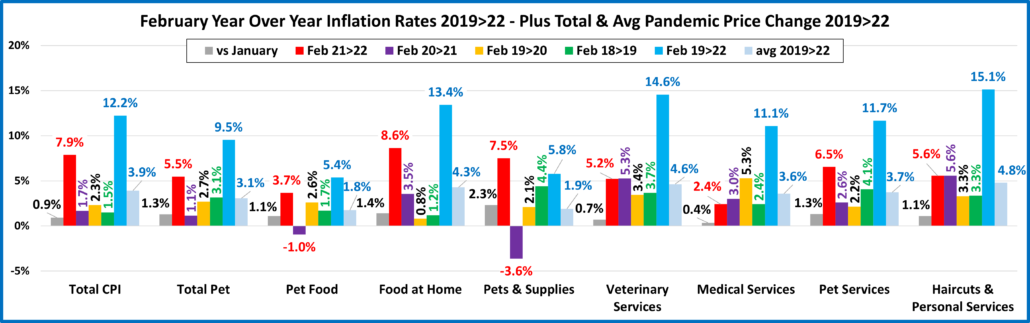
Next, we’ll turn our attention to the Year over Year inflation rate change for the month of April and compare it to last month, last year and to previous years. We’ve added some human categories to put the pet numbers into perspective.
Overall, Prices vs 2021 were up 8.3% vs 2021 with the Grocery increase now hitting 10.8%. There are some small positives. Only 3 of 9 categories had increases over 1% from last month, down from 5 in March…. And Pet Supplies prices actually fell 0.1% from March. There is a little hope.
- U.S. CPI – Prices are up 0.6% from last month. In March the increase was 1.3%. Inflation was 8.3%. The targeted rate is <2%. We remain 4 times higher than the “target”. Inflation is getting worse, but the increase rate has slowed.
- Pet Food – Prices are up 1.2% vs March and 7.0% vs April 2021. They are being measured against a deflationary year, but that increase is more than triple the pre-pandemic 2.2% increase from 2018 to 2019.
- Food at Home – Prices are up 1.3% from March. The increase from 2021 is 10.8%, which is the largest increase in any month since 11.1% in November 1980 and the largest April increase since 12.3% in 1979. Inflation for this category since 2019 is 27% more than the national CPI.
- Pets & Supplies – Prices fell 0.1% from a record high in March. Current prices go against deflated prices in 2021 but their increase only trails Food at Home, Veterinary and the Total CPI. Note: They have the lowest increase since 2019
- Veterinary Services – April prices grew 0.8% from March. This pushed them up 9.8% from 2021, trailing only Food at Home, but more than twice their increase in past years. They stayed on top in the increase since 2019, +18.6%.
- Medical Services – Prices sharply increased at the start of the pandemic in 2020 but then inflation slowed and returned to a more normal rate in 2021. It appears to be turning up again in 2022.
- Pet Services – Inflation slowed in 2020 but began to grow in 2021 & 2022. Prices are up 1.7% from March and 5.9% from 2021, down slightly from a record 6.5% increase in February, but still about double the rate of 2019 & 2020.
- Haircuts & Other Personal Services – Prices are +.4% from March and 5.1% from 2021. They are +15.0% since 2019.
- Total Pet – Inflation is growing and is 3+ times the rate of last year. Veterinary is a big driver but all segments contributed to the +8.1%, which is almost equal to the 8.3% U.S. CPI. Inflation has caused problems in the past by reducing the frequency of purchase in Supplies, Services and Veterinary. Super Premium Food has been generally immune as consumers are used to paying big bucks and it is needed every day. We’ll see if consumers are still willing to pay the higher prices for more discretionary products and services at the same frequency as they did in the past.
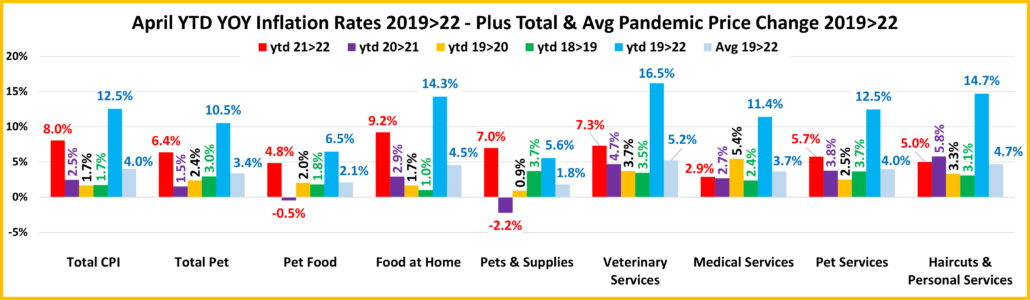
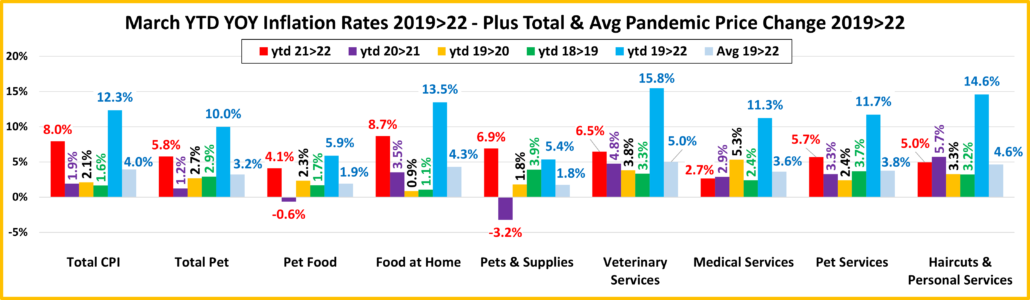
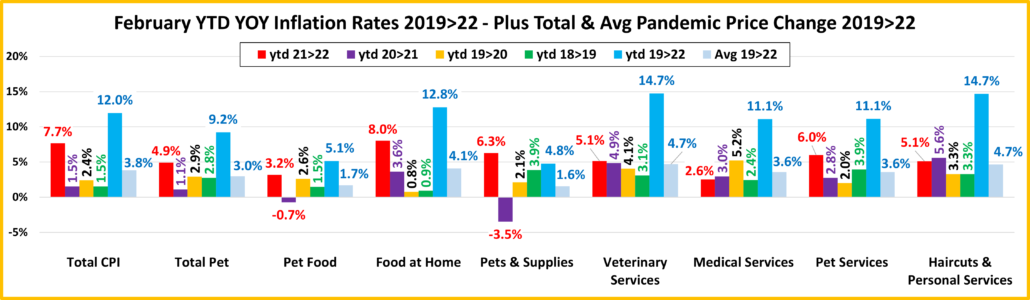
Now here’s a look at Year to Date numbers. How does 2022 compare to previous years…so far?
The increase from 2021 to 2022 is the biggest for 7 of 9 categories. The average annual increase since 2019 is over 3% for all but Pet Food & Pet Supplies. This is due to deflation in 2021.
- U.S. CPI – The current increase is double the average increase from 2019>2022, but over 4 times the average annual increase from 2018>2021. Inflation is a big problem that started recently.
- Pet Food – Inflation is growing stronger, especially after deflation in 2021.
- Food at Home – The 2022 YTD inflation beat the U.S. CPI by 15%. You can see the impact of supply chain issues.
- Pets & Pet Supplies – Despite an April dip, prices are up sharply in 2022. Although the 2021>22 increase is being measured against a deflationary 2021, it is very significant and 2nd to Veterinary in the Pet Industry segments.
- Veterinary Services – Has the most inflation since 2019 and is the only segment on the chart in which the inflation rate has consistently grown each year throughout the pandemic and recovery. No matter what, just charge more.
- Medical Services – Prices went up significantly at the beginning of the pandemic, but the rate has slowed since and has now essentially returned to pre-pandemic levels.
- Pet Services – February was the largest year over year monthly increase in history. The rate slowed in March but turned up again in April. The current YTD increase remains 2nd only to 6.4% in 2009. Demand has grown for Pet Services while the availability has decreased, a formula for inflation.
- Haircuts & Personal Services – The services segments, essential & non-essential were hit hardest by the pandemic. After a small decrease in March, prices turned up 0.4% in April. The YTD rate is now down slightly from 2020>21 but still 60% more than 2018>19. Consumers are paying 14.7% more than in 2019. This usually reduces the frequency.
- Total Pet – When we first looked at the pandemic impact on Petflation. We saw basically two different patterns. Prices in the Services segments continued to increase, and the rate accelerated as we moved into 2021. The product segments – Food and Supplies, were on a different path. They generally deflated in 2020 and didn’t return to 2019 levels until mid-year 2021. Food prices began a slow increase, but Supplies remained stable until we neared yearend. In 2022, everything changed as Food and Supplies prices turned sharply up. In April, the inflation rate grew in all segments but Supplies. This pushed the YTD CPI increase vs 2021 for Total Petflation to 6.4%, 80% of the extraordinarily high 8.0% rate in the overall market. It was only 72.5% of the National rate in March.
Inflation is surging in the Pet Market. Will it impact spending? Let’s put it into perspective. The 6.4% YTD increase in Total Pet is far below the 9.6% record set in 2009 but 4 times larger than the 1.5% avg since then. Although pet spending continues to move to higher income groups, the impact of inflation varies by segment. Supplies is the most affected as many categories are price sensitive. Super Premium Food has become widespread because the perceived value has grown. Higher prices just push people to value shop. Veterinary prices have strongly inflated for years, resulting in a reduction in visit frequency. Spending in the Services segment is driven by higher incomes, so inflation is less impactful. Hopefully, Supplies prices will continue to fall but we’ll just have to wait and see the impact of the strong Petflation.