Retail Channel $ Update – July Monthly & August Advance
In August, Commodities deflation vs last year accelerated to -1.2% from -0.4%. Although still deflating, the high prices from cumulative inflation still impact consumer spending. The YOY Total Retail sales lift for August is 53% of the 92>23 average but the Relevant Retail increase is 73% – Both are radically down from July. Prices are now deflating in many channels but still high vs 21, which can slow growth in the amount of product sold. There is still a long road to recovery, so we’ll continue to track the retail market with data from 2 reports provided by the Census Bureau and factor in a targeted CPI.
The Census Bureau Reports are the Monthly and the Advance Retail Sales Reports. Both are derived from sales data gathered from retailers across the U.S. and are published monthly at the same time. The Advance Report has a smaller sample size so it can be published quickly – about 2 weeks after month end. The Monthly Report includes data from all respondents, so it takes longer to compile the data – about 6 weeks. Although the sample size for the Advance report is smaller, the results over the years have proven it to be statistically accurate with the Monthly reports. The biggest difference is that the full sample in the Monthly report allows us to “drill” a little deeper into the retail channels.
We will begin with the July Monthly Report and then go to the August Advance Report. Our focus is comparing to last year but also 2021 & 2019. We’ll show both actual and the “real” change in sales as we factor inflation into the data.
Both reports include the following:
- Total Retail, Restaurants, Auto, Gas Stations and Relevant Retail (removing Restaurants, Auto and Gas)
- Individual Channel Data – This is more detailed in the Monthly reports, and we’ll focus on Pet Relevant Channels.
The data will be presented in detailed charts to facilitate visual comparison between groups/channels. The charts will show 11 separate measurements. To save space they will be displayed in a stacked bar format for the channel charts.
- Current Month change – % & $ vs previous month
- Current Month change – % & $ vs same month last year and vs 2021.
- Current Month Real change vs last year and vs 2021 – % factoring in inflation
- Current Ytd change – % & $ for this year vs last year, 2021 & 2019.
- Current Ytd Real change % for this year vs last year and vs 2021 and 2019
- Monthly & Ytd $ & CPIs for this year vs last year and vs 2021 which are targeted by channel will also be shown. (CPI Details are at the end of the report)
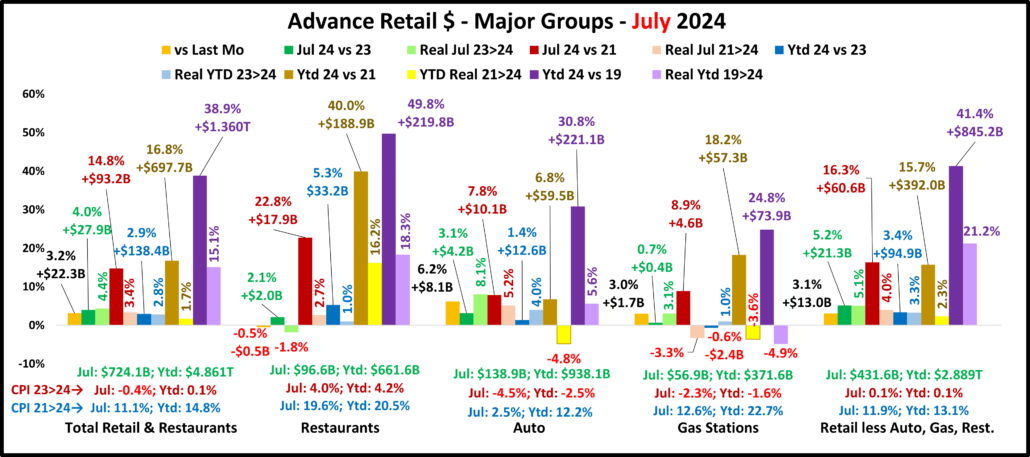
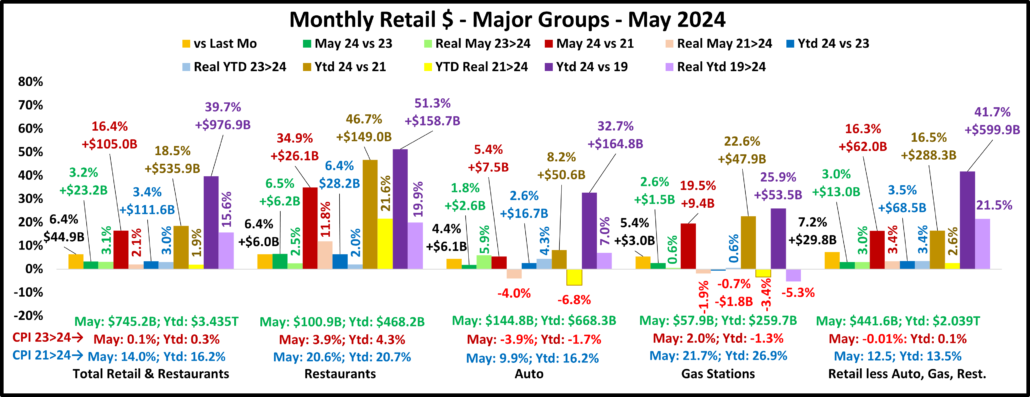
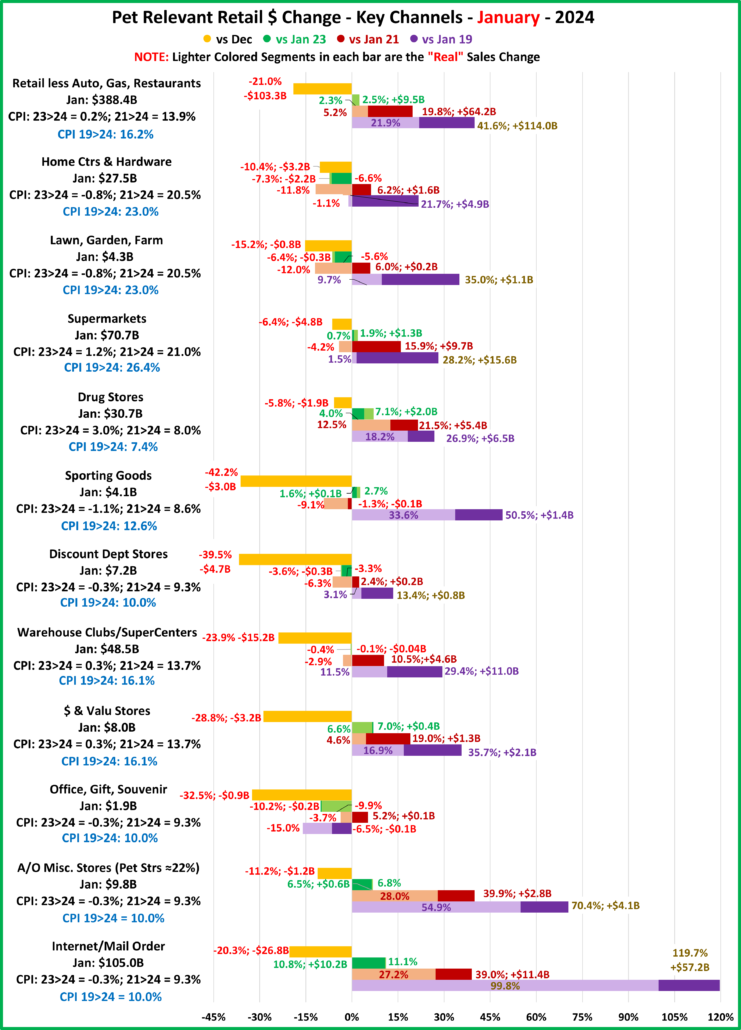
First, the July Monthly. Only Restaurants were down from June and there was only 1 actual sales drop vs 23 & 21. We should note that Gas Stations are still selling less product than in 2019. Also, Relevant Retail is all positive again. They have been all positive in 6 of the last 9 months but only in 2 of the last 5. ($ are Not Seasonally Adjusted)
The July Monthly is $1.7B more than the Advance report. Restaurants: +$0.1B; Auto: +$1.4B; Gas Stations: +$0.4B; Relevant Retail: -$0.1B. In a bit of a surprise. $ales were up vs June for all but Restaurants. A Jun>Jul increase in Total Retail only happens about 50% of the time. The 3.4% lift was also far above the 0.1% avg. There was only 1 drop in actual sales – Ytd vs 23 for Gas Stations. There were 5 “real” sales drops, down from 9 last month. Total and Relevant Retail were both all positive. Restaurants still have the biggest increases vs 21 & 19 but Relevant Retail stayed at the top of “real” performance vs 2019. However, only 51% of their growth is real.
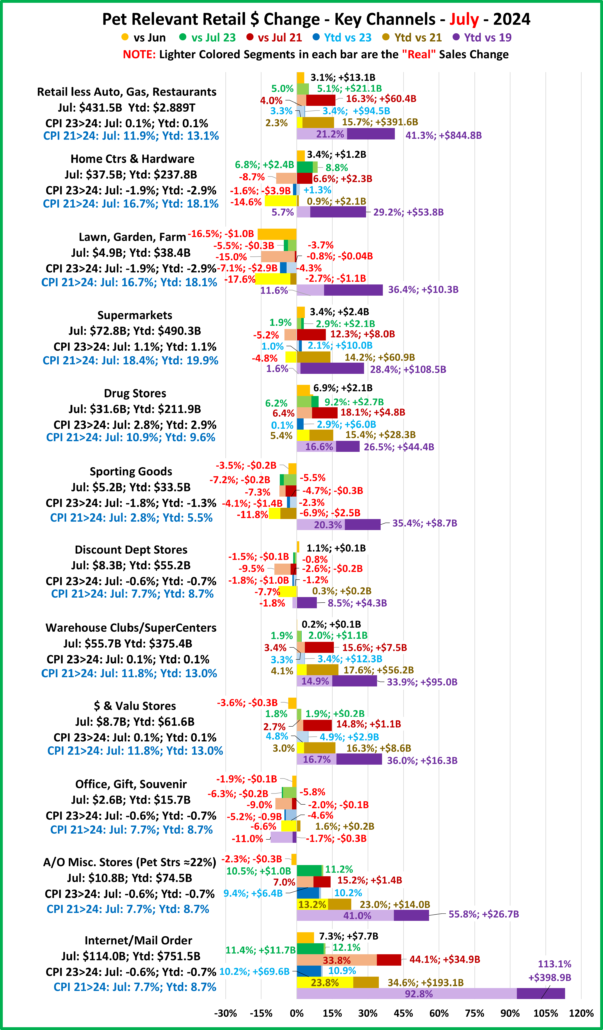
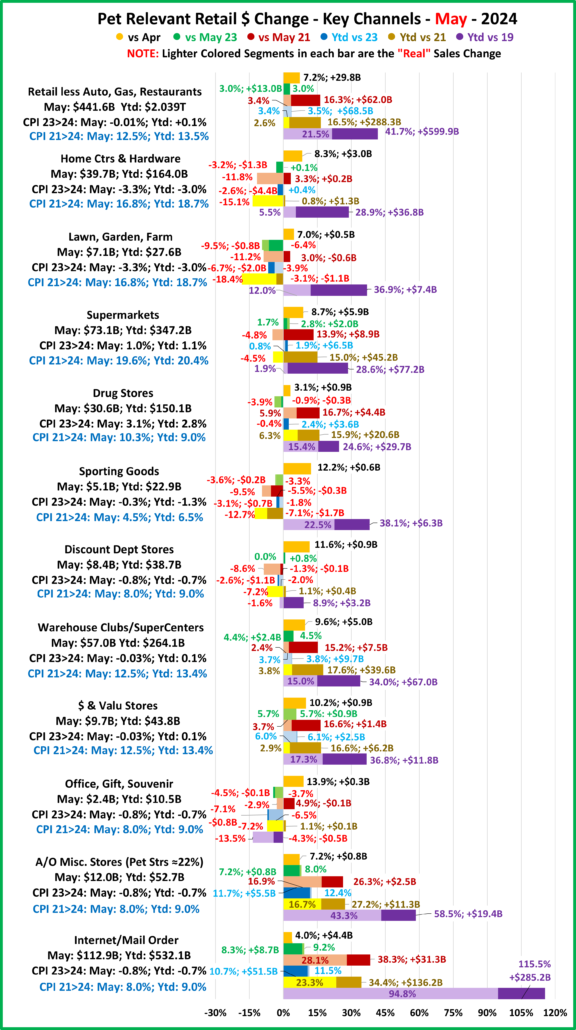
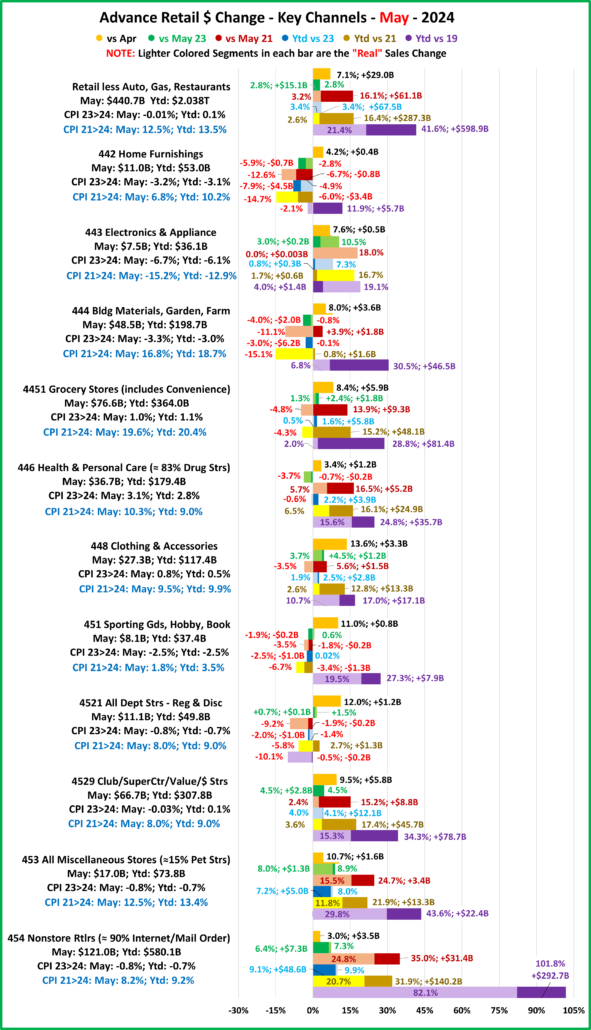
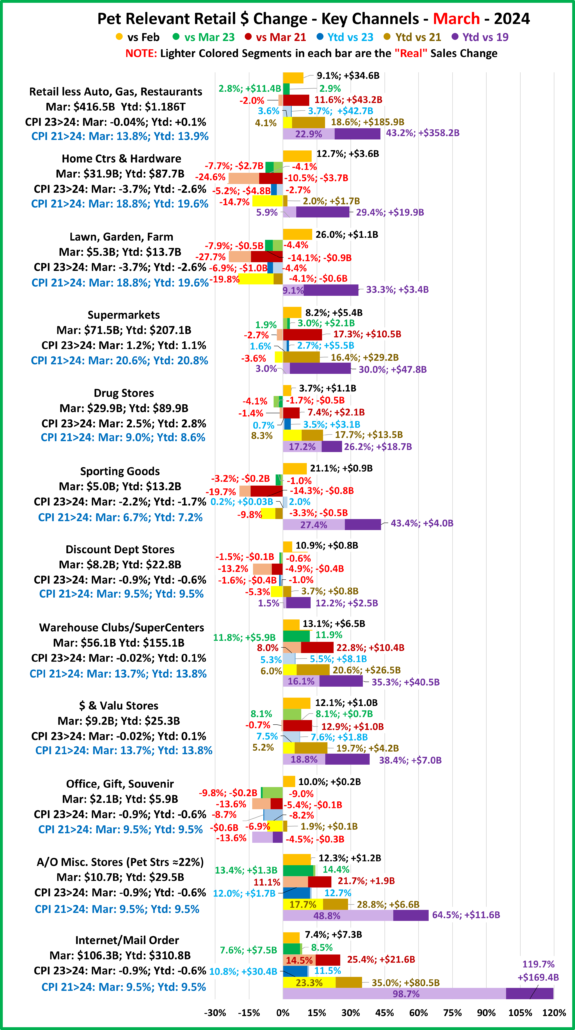
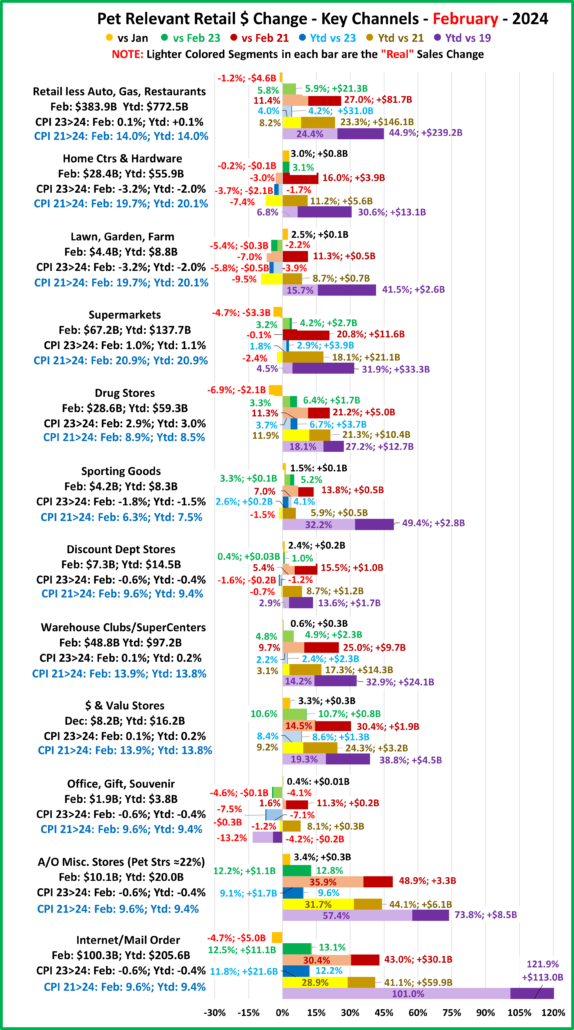
Now, let’s see how some Key Pet Relevant channels did in July in the Stacked Bar Graph Format
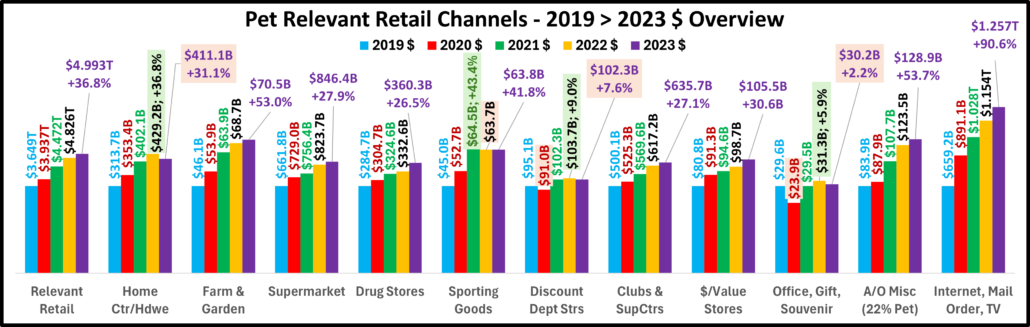
Overall– 6 of 11 were up from June. vs July 23, 7 were both actually and “really” up. Vs July 21, 7 were up but only 5 were real increases. Vs 2019, Off/Gift/Souv were actually & really down and Disc Dept Strs were also really down.
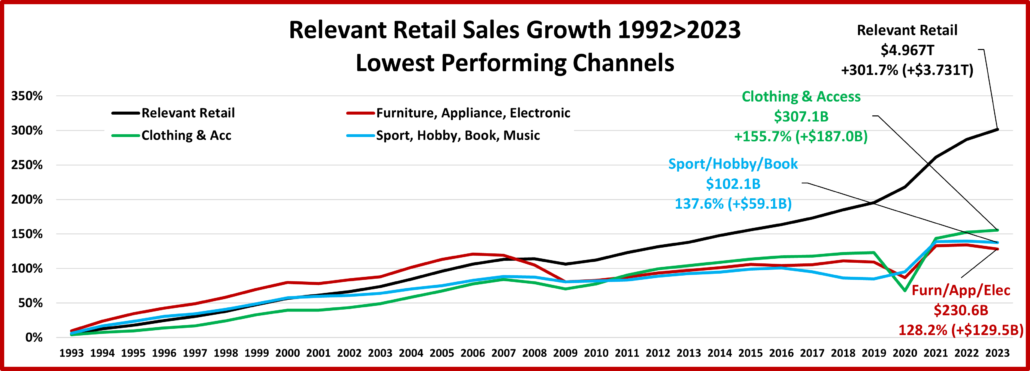
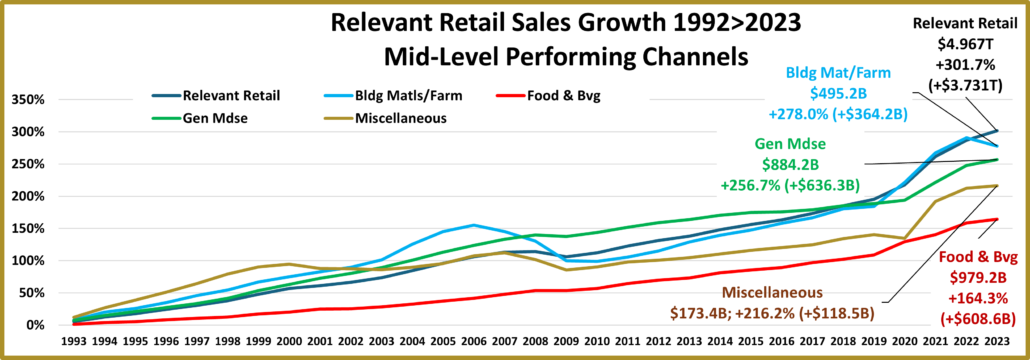
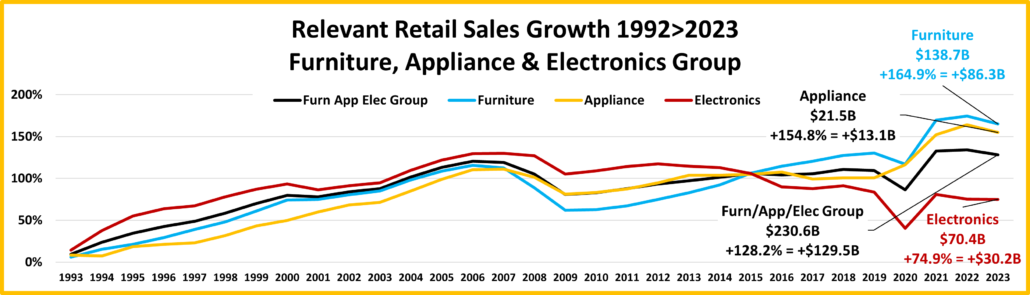
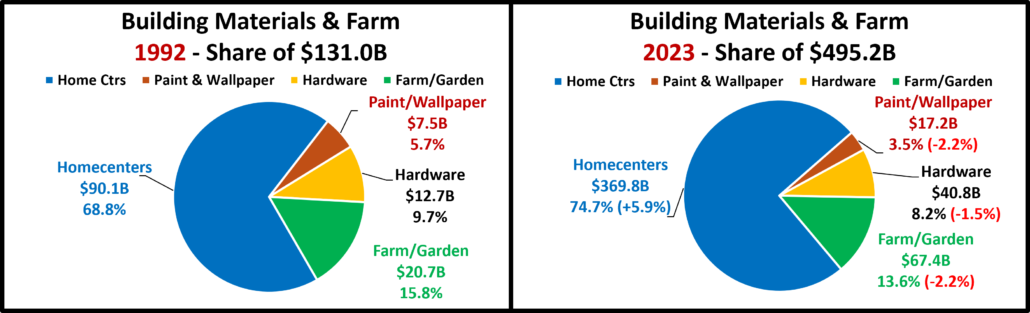
- Building Material Stores – The pandemic focus on home has produced sales growth of 30.5% since 2019. Prices for the Bldg/Matl group have inflated 16.7% since 2021 which is having an impact. HomeCtr/Hdwe are only actually up vs July 23 & 21 and Ytd vs 19, but Farm stores are only actually up Ytd vs 19. Only the “real” measurement vs July 21 is negative for Home/Hdwe. For Farm Stores all “real” numbers but vs 19 are negative. Plus, only 22% of the overall Building Materials group’s 19>24 lift was real. Avg 19>24 Growth: HomeCtr/Hdwe: 5.3%, Real: 1.1%; Farm: 6.4%, Real: 2.2%
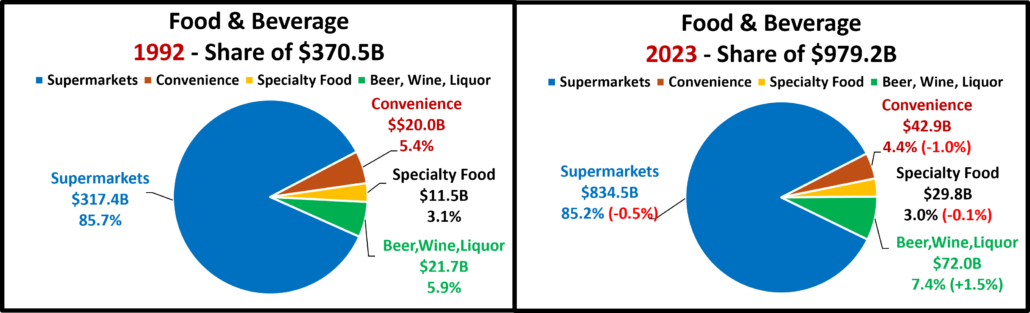
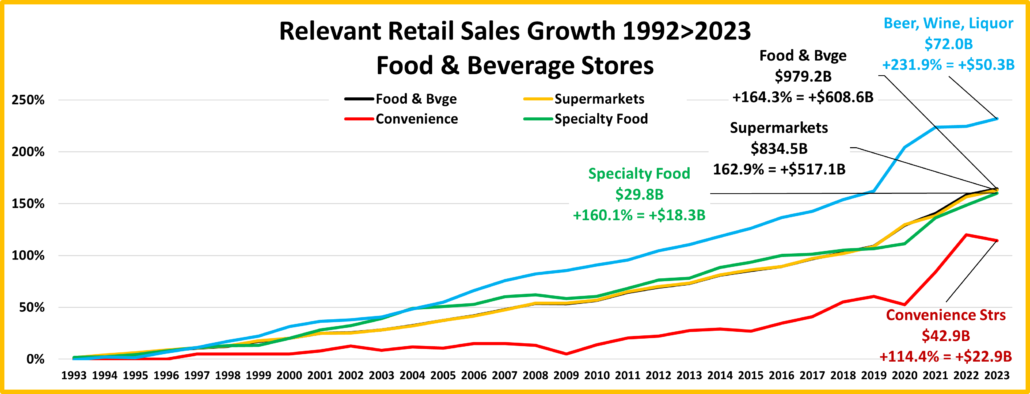
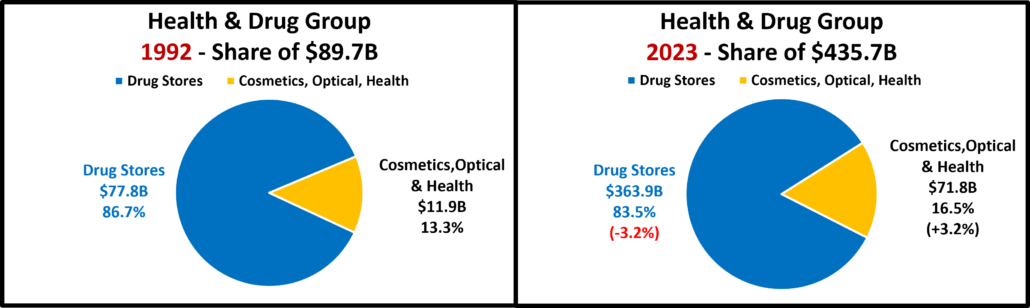
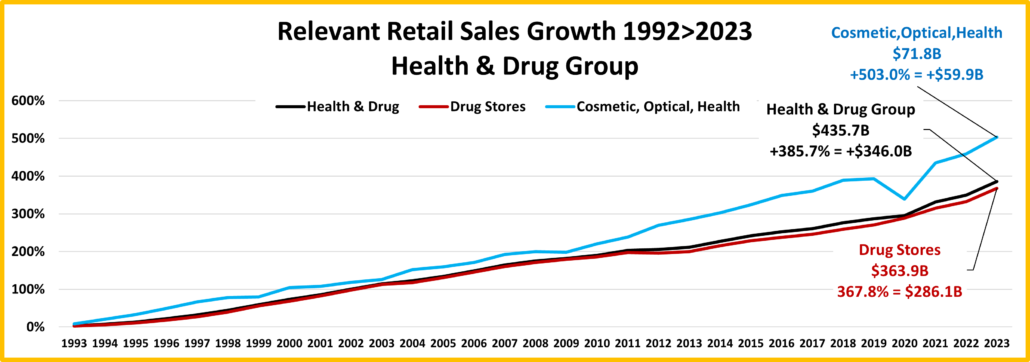
- Food & Drug – Both are truly essential. Except for the pandemic food binge buying, they tend to have smaller changes in $. In terms of inflation, the Grocery rate is only 39% of the rate for Drug/Med products. Drug Stores are positive in all measurements and 63% of their 2019>24 growth is real. Supermarkets’ actual $ are up in all measurements and they are only “really” down vs 2021. However, only 6% of their 19>24 increase is real growth. Avg 19>24 Growth: Supermarkets: +5.1%, Real: +0.3%; Drug Stores: +4.8%, Real: +3.1%.
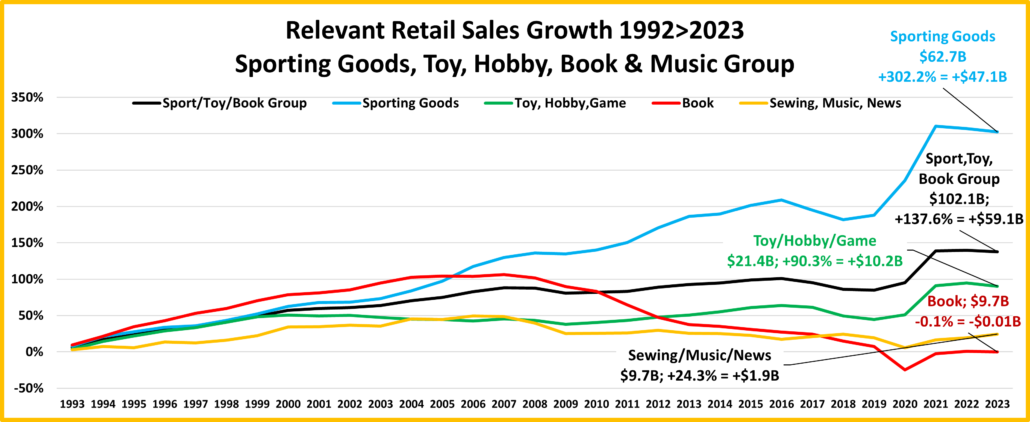
- Sporting Goods Stores – They also benefited from the pandemic in that consumers turned to self-entertainment, especially sports & outdoor activities. Sales are down from June and their only positives are actual & real Ytd vs 19. Prices are still deflating, -1.8% vs 23. Deflation started in April 23 and is a big change from +1.1% in 22>23 and +7.9% in 21>22. The result is that 57% of their 35.4% lift since 19 is real. Avg 19>24 Growth Rate is: +6.2%; Real: +3.8%.
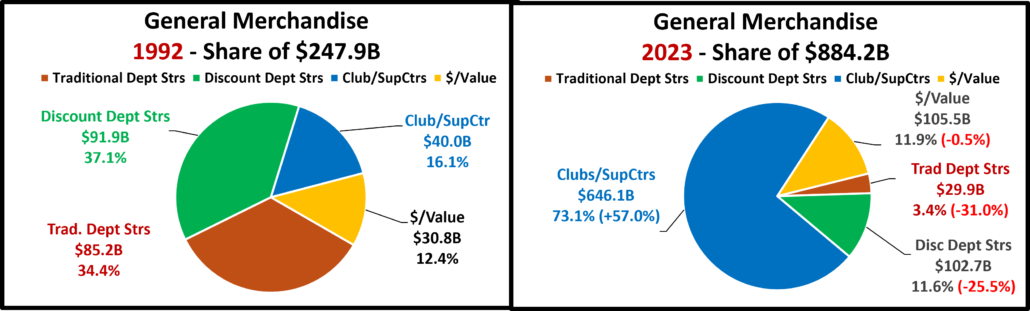
- Gen Mdse Stores – All actual & real sales were up for Club/SupCtrs & $ stores. On the other hand, Discount Dept Stores were only actually up Ytd vs 21 & 19. All real measurements are negative so none of their growth since 2019 is real. The other channels average 44% in real growth. Avg 19>24 Growth: SupCtr/Club: 6.0%, Real: 2.8%; $/Value Strs: +6.3%, Real: +3.1%; Disc. Dept. Strs: +1.6%, Real: -0.4%.
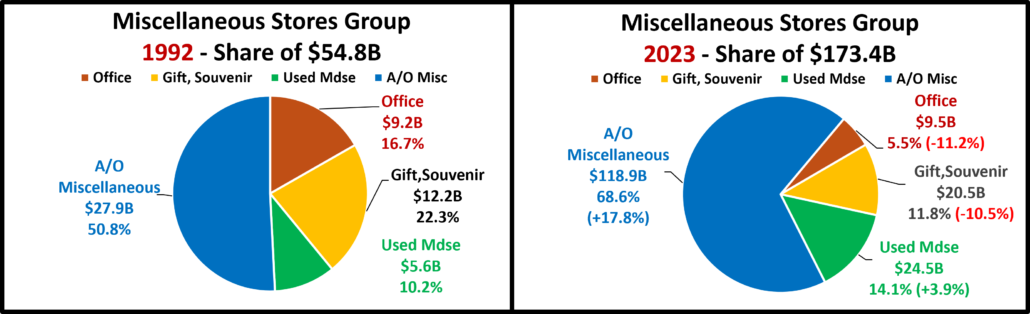
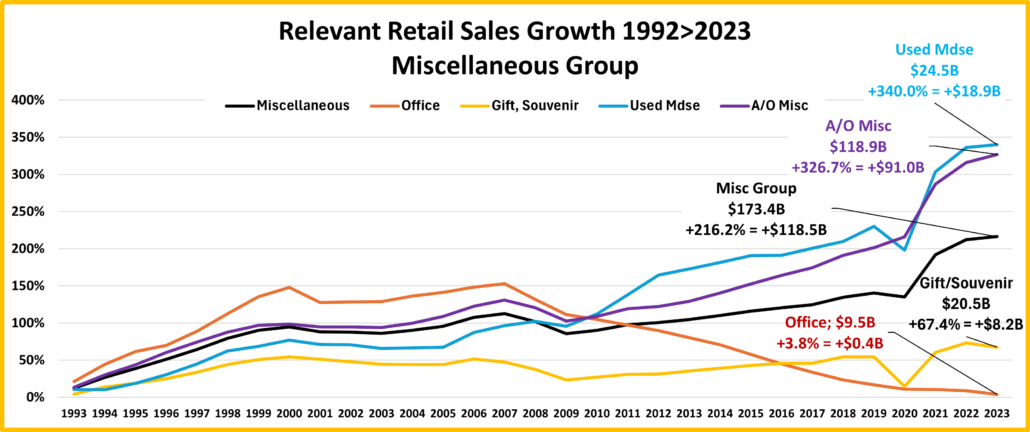
- Office, Gift & Souvenir Stores – Sales were down -1.2% from June. This set the stage for a bad month. They are only actually up Ytd vs 21. All of their real sales numbers including Ytd vs 2019 are negative. Their recovery started late, and their slow progress has been stalled since June 23. Avg Growth Rate: -0.3%, Real: -2.3%
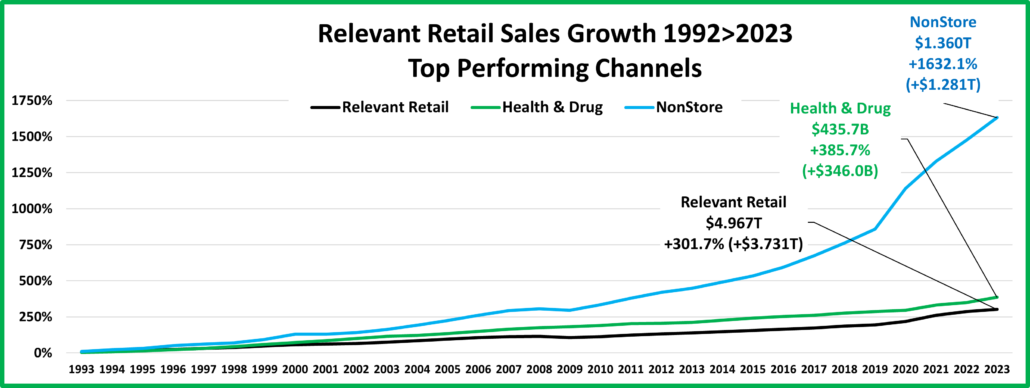
- Internet/Mail Order – Sales are +7.3% from June and set a new monthly record of $113.95B. All measurements are positive, but their growth (+10.2%) is still only 63% of their average since 2019. However, 82.0% of their 113.1% growth since 2019 is real. Avg Growth: +16.3%, Real: +14.0%. As expected, they are still by far the growth leader since 2019.
- A/O Miscellaneous – Pet Stores are 22>24% of total $. In May 2020 they began their recovery which reached a record level of $100B for the first time in 2021. In 2022 their sales dipped in January, July, Sept>Nov, rose in December, fell in Jan>Feb 23, grew Mar>May, fell in Jun>Aug, rose in Sep>Nov, fell in Dec>Jan, grew in Feb>May, then fell in Jun>Jul. However, all measurements are positive. They are still in 2nd place, behind the Internet, in the % increase vs 19 and vs 21. Also, 73% of their 56.6% growth since 2019 is real. Average 19>24 Growth: +9.4%, Real: +7.2%.
July brought an unusual lift as 6 small channels were up vs June. The YOY lift for Total Retail was only -9% below Avg as 7 of 11 smaller channels and all big groups were up vs July 23. Prices are deflating in 7 of 11 channels but cumulative inflation is still a factor. Many sales lifts are lower as 6 of 11 channels were really down vs July 21. The Retail Recovery may be growing again. The commodities CPI fell to -1.2% in August. Let’s see if continuing deflation impacts Retail $ales.
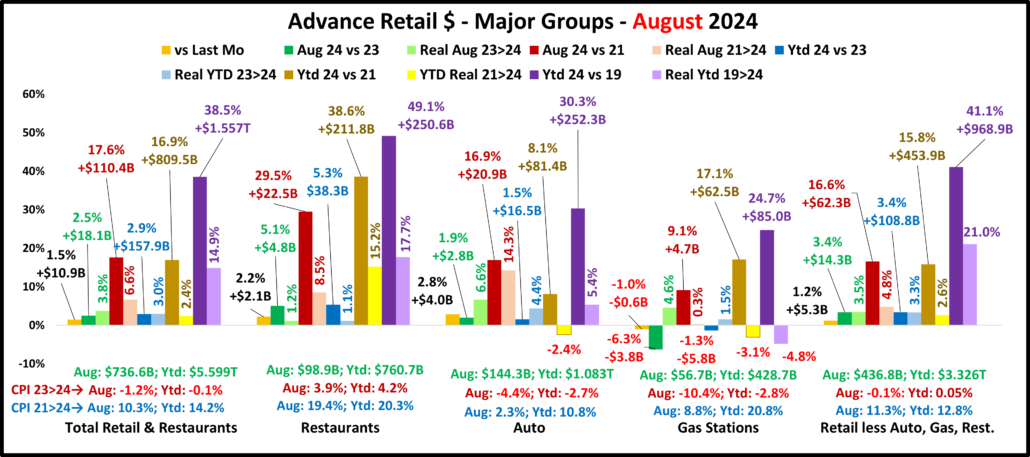
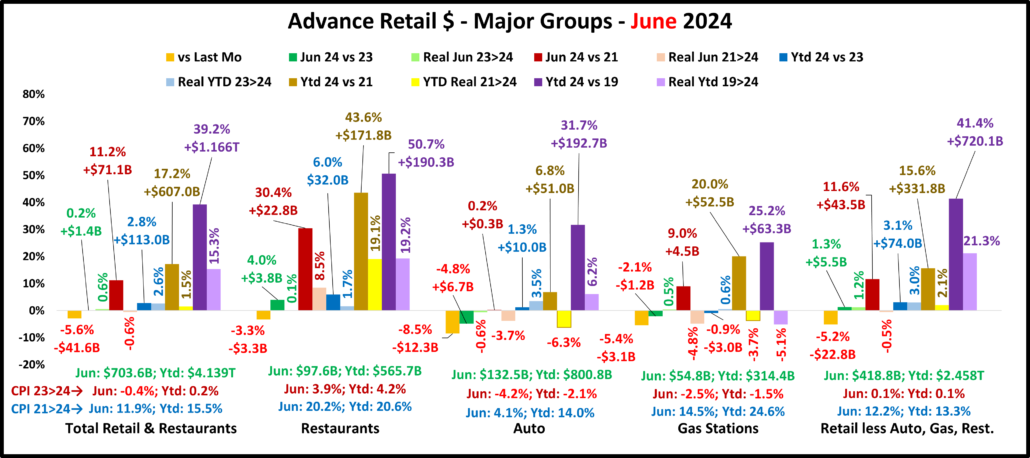
August sales vs July increased for all but Gas Stations. A Jul>Aug Total Retail lift has happened in 78% of the years since 1992. However, the 1.5% lift is -32% below average. All actual YOY $ measurements are positive for all groups but Gas Stations. The Relative Retl lift vs Aug 23 was -27% below their 92>23 Average. The lifts for Tot Retl, Restaurants & Auto were also well below avg. Inflation is still a big factor. The CPI for all commodities, the best pricing measure for Retail, dropped to -1.2% but is 10.3% vs 21. There is some “real” retail good news. In July, 4 measurements were “really” down vs 23 & 21. In August, only 2 were really down, Auto & Gas Stations Ytd vs 21. Total & Relevant Retl & Restaurants were all positive. Of note: from Nov 23>Feb 24 Relevant Retail had 4 straight months of all positive measurements. After 2 months with a negative, they have been all positive in 3 of the last 4 months. Total Retail has the same Apr>Aug pattern.
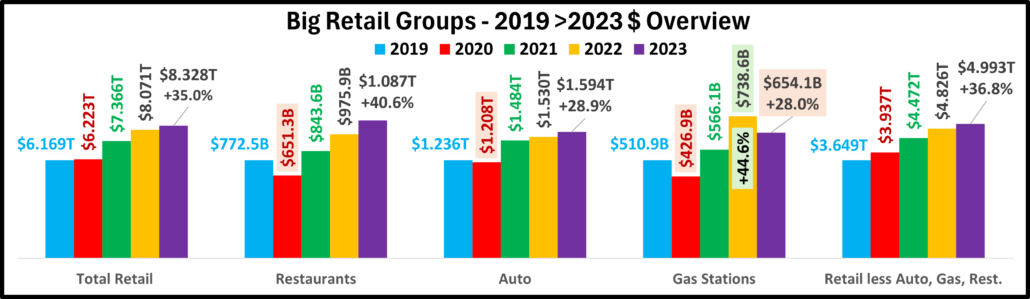
Overall – Inflation Reality – For Total Retail, deflation increased to -1.2% and all measurements were again positive. For Restaurants, inflation remains high, +3.9% but they are again all positive. Gas prices fell but that group is still in turmoil. Auto prices are still falling and are only +2.3% vs 21 which helped actual & real sales. Inflation fell to -0.1% for Relevant Retail and sales are again all positive. Their progress appears to be getting back on track.
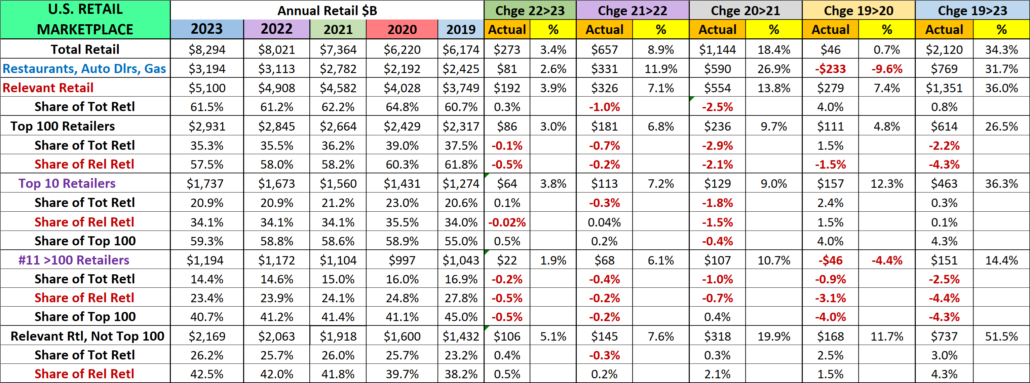
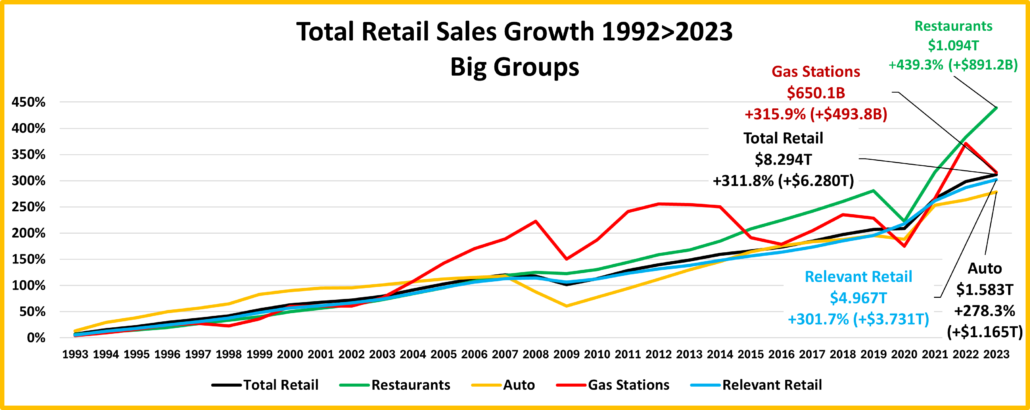
Total Retail – Since June 20, every month but April 23 & June 24 has set a monthly sales record. In 2023, Sales were on a roller coaster. Up Jul>Aug, down Sept, up Oct>Dec, down Jan 24, up Feb>Mar, down April, up May, down June, up in Jul>Aug. Prices are now -1.2%. Monthly YOY sales growth is only 52% of the 92>23 avg. Sales are up 2.9% Ytd vs 2023, only 43% of their avg 19>24 growth. Plus, only 39% of the 19>24 growth is real. YOY inflation in Total Retail has slowed and is still deflating but we still see its cumulative impact. Growth: 23>24: 2.9%; Avg 19>24: +6.7%, Real: +2.8%.
Restaurants – They were hit hard by the pandemic and didn’t begin recovery until March 2021. However, they have had strong growth since then, exceeding $1T for the 1st time in 2023 and set another monthly sales record in August. They have the biggest Ytd increases vs 23, 21 & 19 and are again positive in all measurements. Inflation slowed to 3.9% in August but is still +19.4% vs 21 and +26.7% vs 19. 36.0% of their 49.1% growth since 19 is real and they remain 3rd in performance behind Relevant & Total. Recovery started late but inflation started early. Growth: 5.3%; Avg 19>24:+8.3%, Real: +3.3%. They just account for 13.6% of Total Retail $, but their performance has helped Total Retail.
Auto (Motor Vehicle & Parts Dealers) – They actively worked to overcome the stay-at-home attitude with great deals and a lot of advertising. They finished 2020 up 1% vs 2019 and hit a record $1.48T in 2021 but much of it was due to skyrocketing inflation. In 22, sales got on a rollercoaster. Inflation started to drop mid-year, but it caused 4 down months in actual sales which are the only reported sales negatives by any big group in 21>22. This is bad but their Y/E real 2022 sales numbers were much worse, down -8.2% vs 2021 and -8.9% vs 2019. 2023 was a true rollercoaster but the $ set a new record, $1.595T. $ fell in Jan 24, grew Feb>Mar, fell in Apr, grew in May, fell in June, grew in Jul>Aug. Only Real Ytd vs 21 is negative. Their CPI is -4.4%. Only 17.8% of 19>24 growth is real. Growth: 1.5%; Avg 19>24: +5.4%, Real: +1.1%.
Gas Stations – Gas Stations were hit hard by “stay at home”. They started recovery in March 2021 and inflation began. Sales got on a rollercoaster in 2022 but reached a record $583B3. Inflation started to slow in August and prices slightly deflated in Dec & Feb 23, then strongly fell in Mar>Jul to -20.2%. In August they rose to -3.7%. In Sep they were +2.7% but began deflating to -4.2% in Feb. In Mar>May they grew, fell in June, rose in July, then fell in August. $ are down monthly & Ytd vs 23. Real sales are down Ytd vs 21 and 19. Growth: -1.3%; Avg 19>24: +4.5%, Real: -1.0%. They show the cumulative impact of inflation and demonstrate how deflation can be both a positive and a negative.
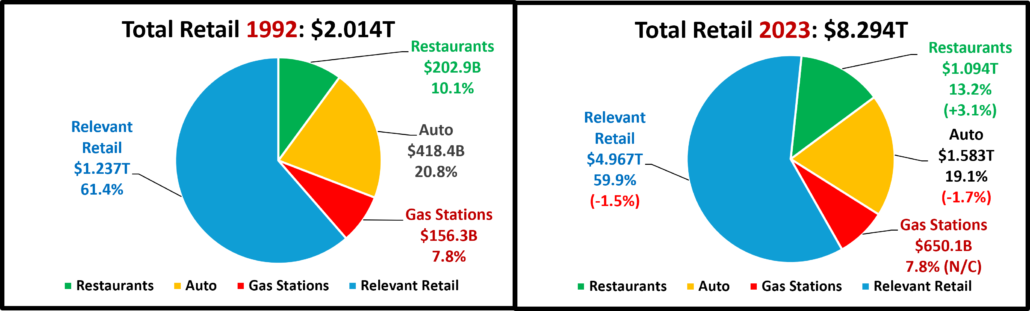
Relevant Retail – Less Auto, Gas and Restaurants – They account for ≈60% of Total Retail $ in a variety of channels, so they took many different paths through the pandemic. However, their only down month was April 2020, and they led the way in Total Retail’s recovery. Sales got on a roller coaster in 2022, but all months set new records with December reaching a new all-time high, $481B, and an annual record of $4.81T. In 2023, the roller coaster continued. A December lift set a new monthly record of $494.7B & an annual record of $4.997T. Sales fell in Jan>Feb 24, rose in Mar, fell in Apr, rose in May, fell in June, then rose in Jul>Aug, a normal pattern. The August YOY lift of 3.4% is -27% below their 92>23 avg but all measurements are again positive. Also, 51% of their 41.1% 19>24 growth is real – #1 in performance. Growth: 3.4%; Avg 19>24: +7.1%, Real: +3.9%. This is where America shops. They finished 2023 and started up 2024 strong. In Mar>Apr their recovery slowed. In May, things improved, worsened in June, rebounded in July, then stabilized in August.
Inflation is still low, but the cumulative impact is still there. Sales increases are still below average. However, the overall situation is improving. It is very significant that there are only 2 real drops vs 23 & 21. There were 8 in June. Restaurants bounced back and the Auto group is still improving. Gas Stations remain in turmoil. The biggest concern is still with Relevant Retail. Their YOY Sales increase slowed but all measurements are positive for the 3rd time in the last 4 months. Total Retail has a similar pattern. After a bad June, the recovery appears to be getting “back on track” in Jul>Aug.
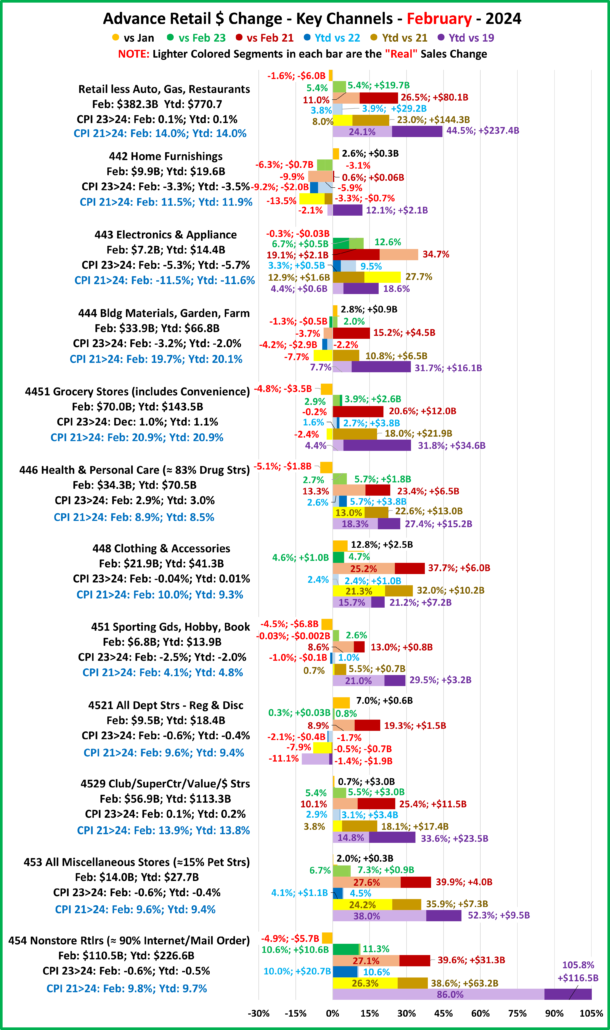
Here’s a more detailed look at August by Key Channels in the Stacked Bar Graph Format
- Relevant Retail: Growth: +3.4%; Avg: +7.1%, Real: +3.9%. 9 were up from July. Vs Aug 23: 8 were up, Real: 10, Vs Aug 21: 7 were up, Real: 6. Vs 19: Only Dept Stores were actually & really down. Furnishing stores were also really down.
- All Department Stores – This group was struggling before the pandemic hit them hard. They began recovery in March 2020. Sales are up 9.1% from July. Their actual $ are only up Ytd vs 21 and the only positive real number is vs August 23. They are even actually & really down vs 2019. Growth: -1.3%; Avg 19>24: -0.2%, Real: -2.2%.
- Club/SuprCtr/$- They fueled a big part of the recovery because they focus on value which has broad consumer appeal. $ales are +4.7% from July, and they are positive in all measurements. However, only 44.4% of their 34.2% 19>24 lift is real – inflation’s impact. Ytd growth is below Avg for the 5th straight month. Growth: 3.8%; Avg: +6.1%, Real: +2.9%.
- Grocery- These stores depend on frequent purchases, so except for the binge buying in 2020, their changes are usually less radical. Actual $ are +0.1% from July and positive in other comparisons. However, cumulative inflation has hit them hard. Real $ are only up vs 23 & 19 and only 5% of 19>24 growth is real. Growth: 1.9%; Avg 19>24: +5.1%, Real: +0.3%.
- Health/Drug Stores – Many stores are essential, but consumers visit less frequently than Grocery stores. $ are +2.5% from July. They are up in all actual comparisons and only really down Ytd vs 23. Because inflation has been relatively low, 63% of their 27.0% growth from 2019 is real. Growth: 2.7%; Avg 19>24: +4.9%, Real: +3.2%
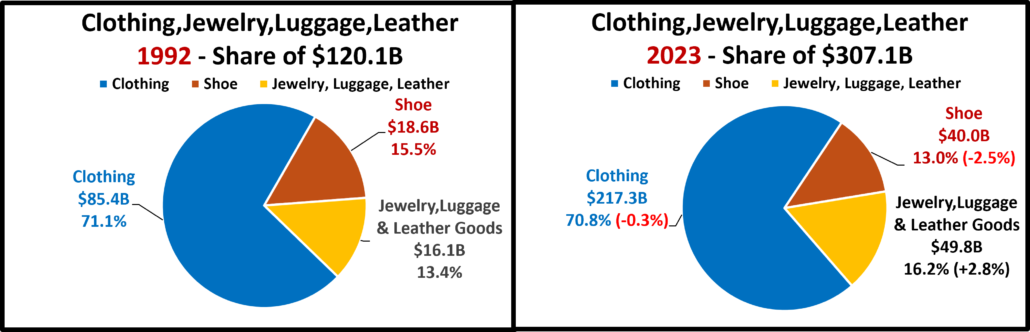
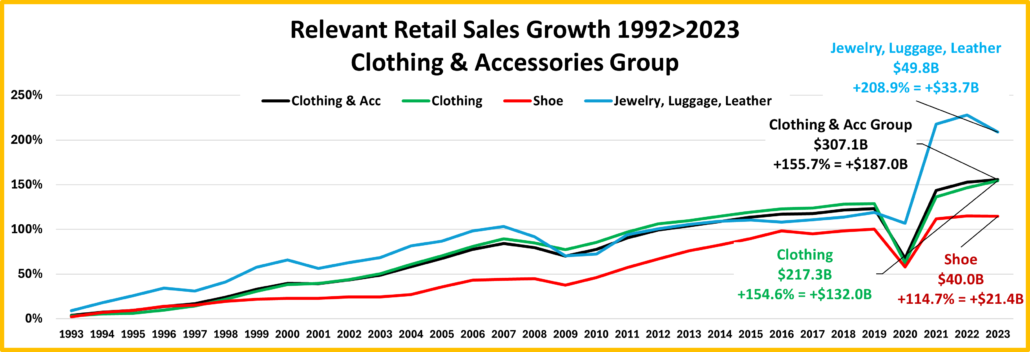
- Clothing and Accessories – Clothes initially mattered less when you stayed home. That changed in March 2021 with strong growth through 2022. Sales are up 7.5% from July and positive in all comparisons but real Ytd vs 21. Plus, 62% of their 19>24 growth is real. Growth: 2.6%; Avg 19>24: +3.2%, Real:+2.0%
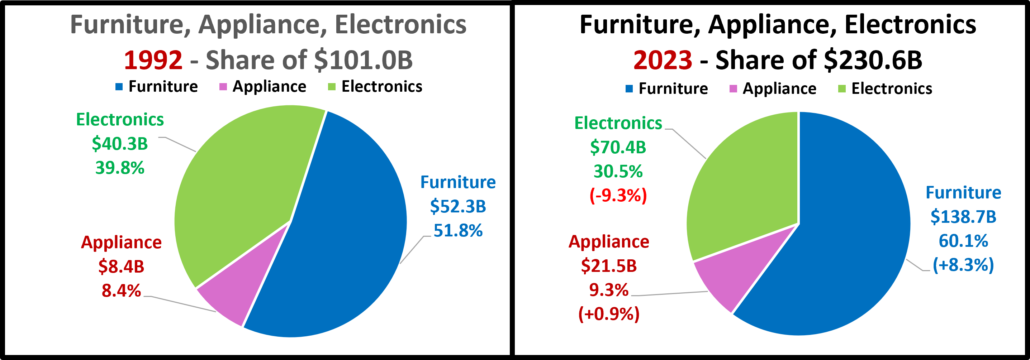
- Home Furnishings – In mid-2020 consumers’ focus turned to their homes and furniture became a priority. Prices are still deflating but they were high in 2022. Sales are +4.5% from July but negative in all measurements but actual vs 2019 & actual & real vs Aug 23. They have sold less product in 2024 than 2019. Growth: -5.1%; Avg 19>24: +2.4%, Real: -0.2%
- Electronic & Appliances – This channel has had many issues. Sales fell in Apr>May of 2020 and didn’t reach 2019 levels until March 21. $ are +2.9% from July and they are only negative in Ytd actual sales vs 21. We should also note that they are the only channel with Ytd growth above their 19>24 avg. Growth: +1.7%; Avg 19>24: +0.9%, Real: +3.8%.
- Building Material, Farm & Garden & Hardware –They truly benefited from the consumers’ focus on home. In 2022 the lift slowed as inflation grew to double digits. Prices are still deflating but sales are -2.6% from July. Actual sales are only down monthly and Ytd vs 23. Prices are deflating but they are still 15.8% above 21 so real sales vs August & Ytd 21 are negative. Also, just 23% of their 19>24 sales growth is real. Growth: -2.3%; Avg 19>24: +5.5%, Real: +1.4%.
- Sporting Goods, Hobby and Book Stores – Consumers turned their attention to recreation and Sporting Goods stores sales took off. Book & Hobby Stores recovered more slowly. After a big June lift sales fell -1.5% in July but rebounded +11.5% in August. All comparisons, actual & real, but Ytd vs 2019 are negative. Their inflation rate has been lower than most groups so 71% of their 24.6% growth since 2019 is real. Growth: -3.5%; Avg 19>24: +4.5%, Real: +3.3%.
- All Miscellaneous Stores – Pet Stores have been a key part of the strong and growing recovery of this group. They finished 2020 at +0.9% but sales took off in March 21 and have continued to grow. Sales are +2.9% vs July and positive in all measurements vs 23, 21 & 19. They are still 2nd in the % increase vs 19 but fell to 3rd vs 21. 67.2% of their 40.8% 19>24 growth is real, but their current Ytd lift is still 11% below Avg. Growth: +6.3%; Avg 19>24: +7.1%, Real: 5.0%.
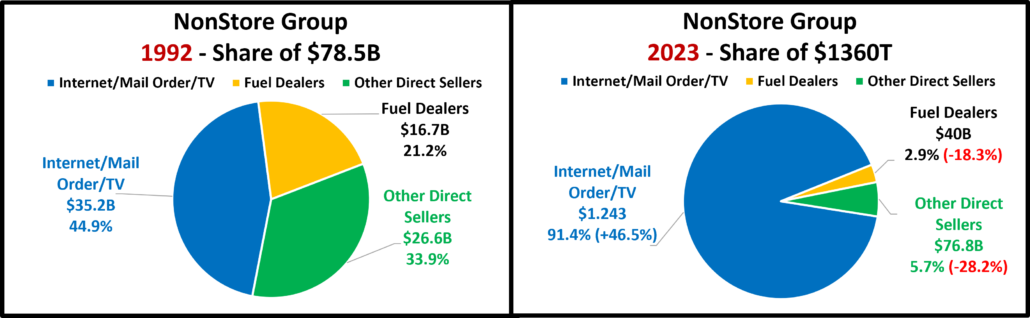
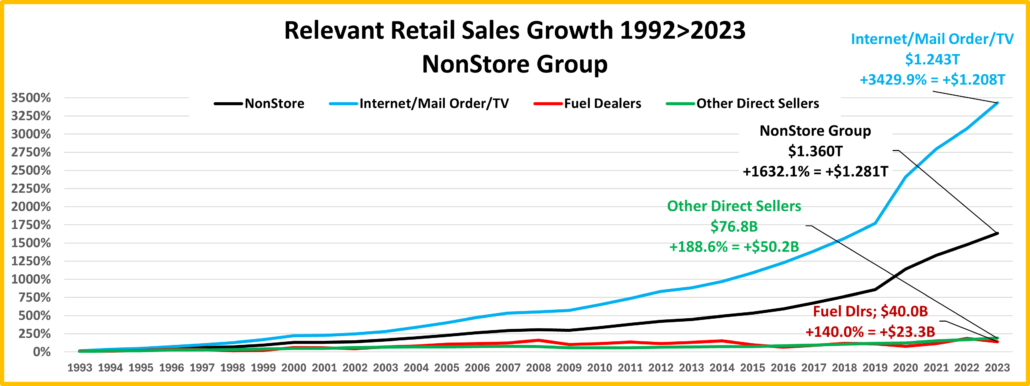
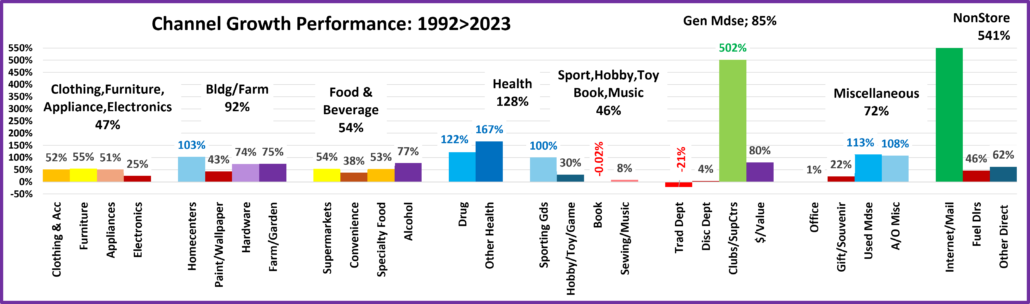
- NonStore Retailers – 90% of their $ comes from Internet/Mail Order/TV. The pandemic accelerated online spending. They ended 2020 +21.4%. The growth continued in 2021 as sales exceeded $100B for the 1st time and they broke the $1 Trillion barrier. $ are -2.0% from July. Their YOY lift fell to +5.6% in August and Ytd they are 44% below Avg. They are positive in all measurements and 81% of their 99.9% 19>24 growth is real. Growth: 8.3%; Avg: +14.9%, Real: +12.6%.
Note: Almost without exception, online sales by brick ‘n mortar retailers are recorded with their regular store sales.
Recap – The Retail recovery from the pandemic was largely driven by Relevant Retail and by the end of 2021 it had become very widespread. In 2022, there was a new challenge, the worst inflation in 40 years. Overall, inflation has slowed considerably from its June 22 peak and now 8 channels are deflating. This should help the Retail Situation. Sales grew from July but the 1.2% lift for Relevant Retail was -58% below their 3.0% 92>23 avg. This was a big drop from last month. However, the big problem has been slowing YOY monthly increases. That temporarily changed in July as the YOY lift vs 23 was 11% above their 92>23 average increase. In August, the 3.4% lift vs 23 was -27% below average. However, only 3 of 11 channels had a $ decrease and 10 of 11 sold more product in 2024 than in 2023. In August, there were 3 channels with lifts of 6.5+%. In July there were 4, but only 1 in June. One channel, Electronics/Appliances again had a Ytd lift above their 19>24 Avg. There is more good news. Relevant Retail is again positive in all comparisons. That’s now happened in 3 of the last 4 months. The recovery definitely slowed in June, but it strongly restarted in July and continued in August.
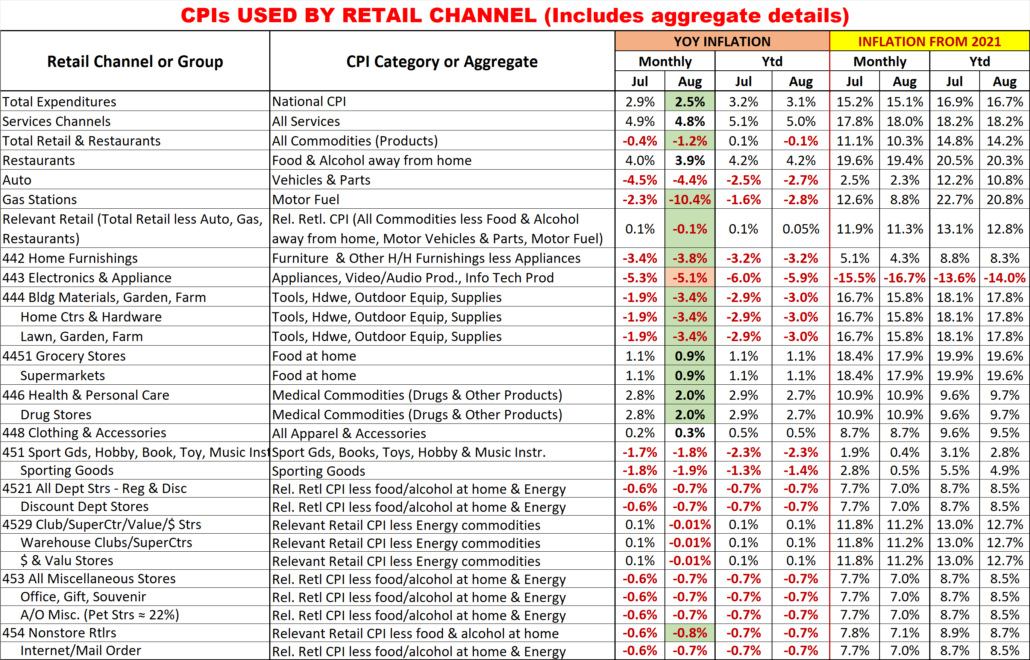
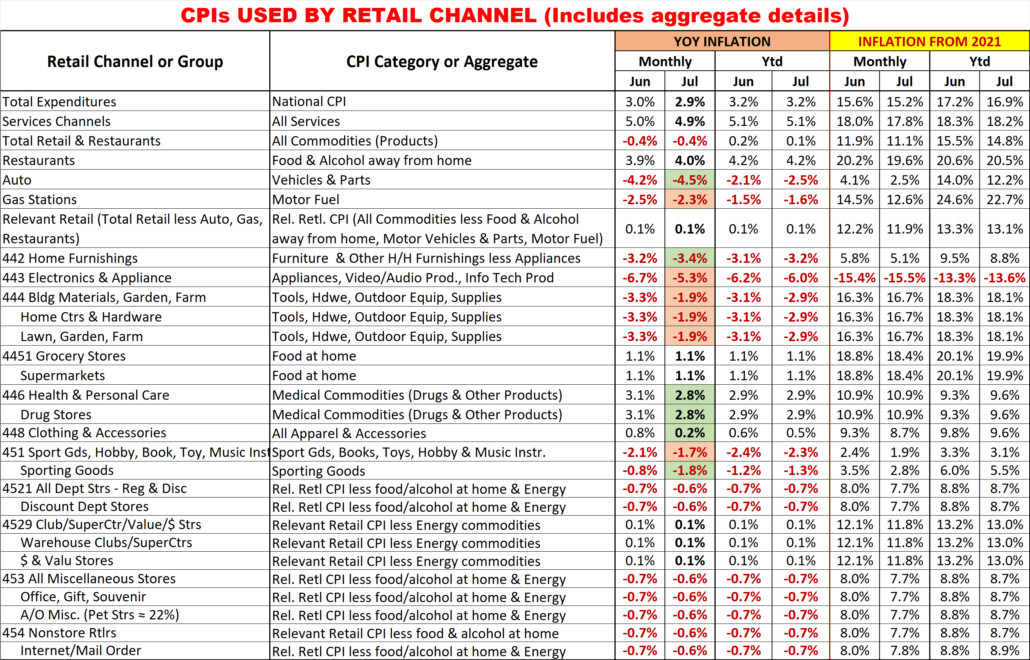
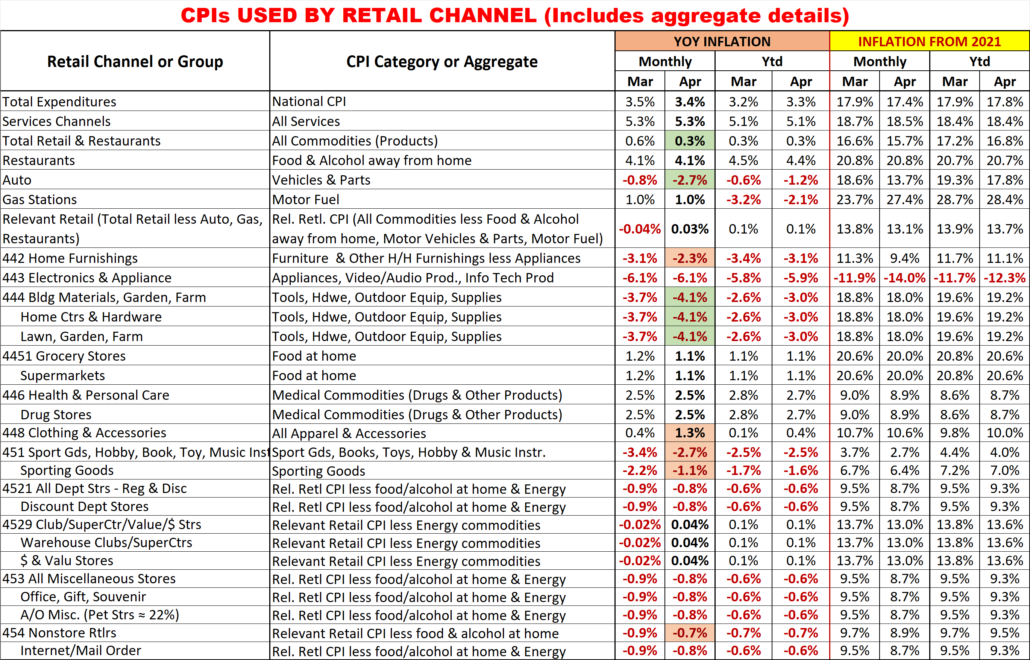
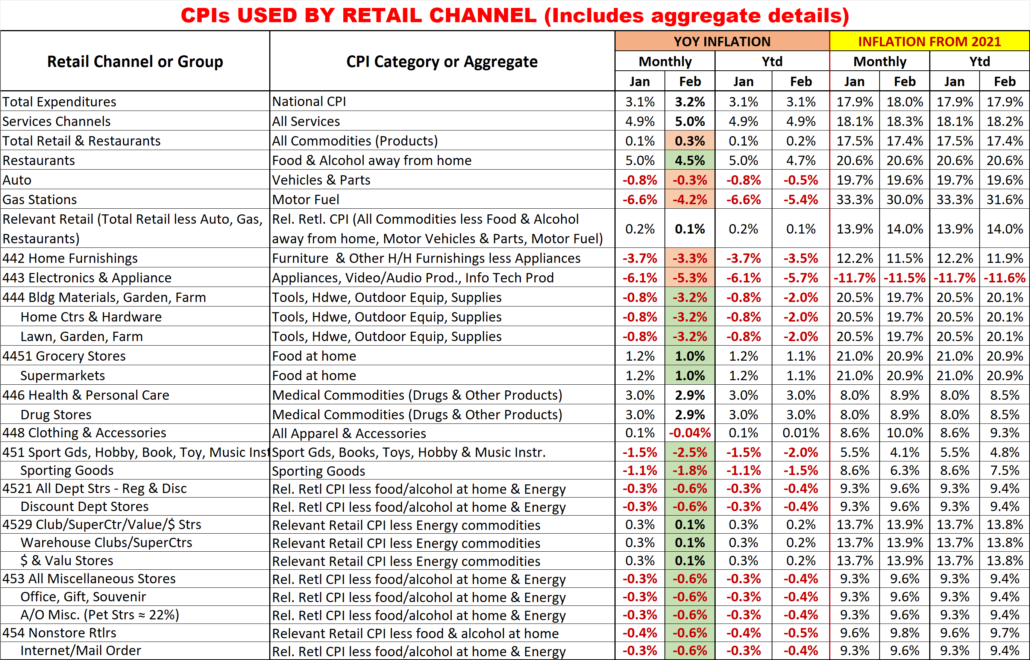
Finally, here are the details and updated inflation rates for the CPIs used to calculate the impact of inflation on retail groups and channels. This includes special aggregate CPIs created with the instruction and guidance of personnel from the US BLS. I also researched data from the last Economic Census to review the share of sales by product category for the various channels to help in selecting what expenditures to include in specific aggregates. Of course, none of these specially created aggregates are 100% accurate but they are much closer than the overall CPI or available aggregates. The data also includes the CPI changes since 2021 to show cumulative inflation.
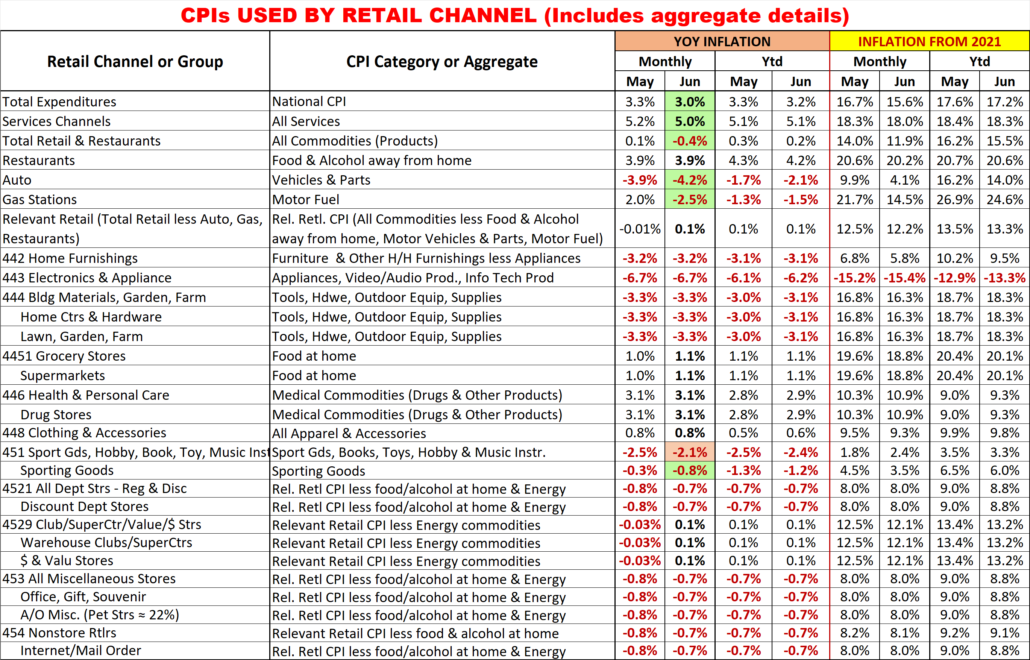
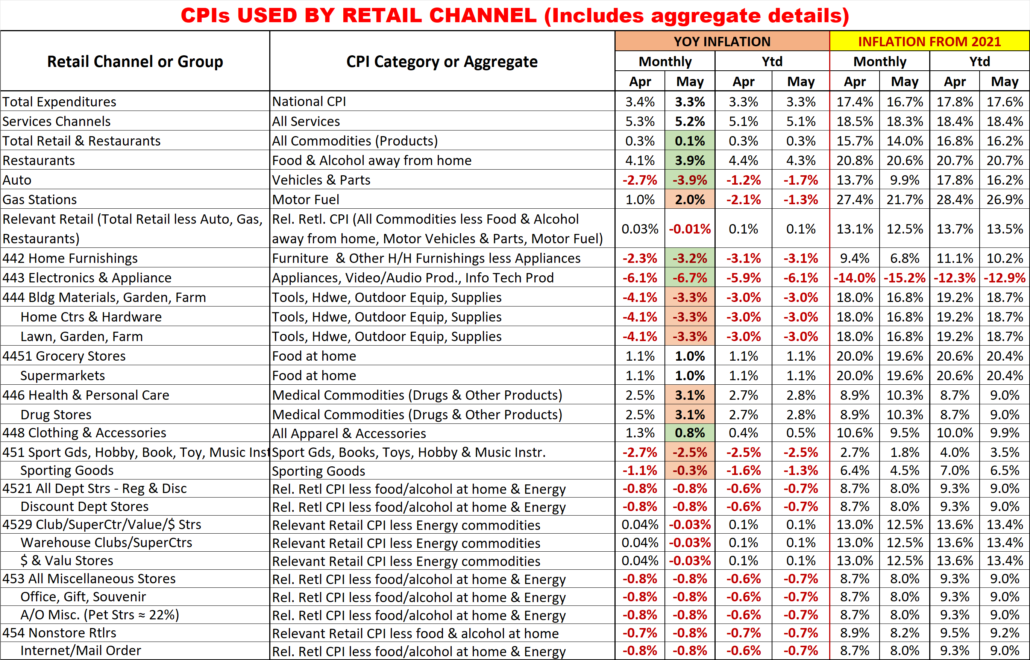
Monthly YOY CPI changes of 0.2% or more are highlighted. (Green = lower; Pink = higher)
I’m sure that this list raises some questions. Here are some answers to some of the more obvious ones.
- Why is the group for Non-store different from the Internet?
- Non-store is not all internet. It also includes Fuel Oil Dealers, the non-motor fuel Energy Commodity.
- Why is there no Food at home included in Non-store or Internet?
- Online Grocery purchasing is becoming popular but almost all is from companies whose major business is brick ‘n mortar. These online sales are recorded under their primary channel.
- 6 Channels have the same CPI aggregate but represent a variety of business types.
- They also have a wide range of product types. Rather than try to build aggregates of a multitude of small expenditure categories, it seemed better to eliminate the biggest, influential groups that they don’t sell. This method is not perfect, but it is certainly closer than any existing aggregate.
- Why are Grocery and Supermarkets only tied to the Grocery CPI?
- According to the Economic Census, 76% of their sales comes from Grocery products. Grocery Products are the driver. The balance of their sales comes from a collection of a multitude of categories.
- What about Drug/Health Stores only being tied to Medical Commodities.
- An answer similar to the one for Grocery/Supermarkets. However, in this case Medical Commodities account for over 80% of these stores’ total sales.
- Why do SuperCtrs/Clubs and $ Stores have the same CPI?
- While the Big Stores sell much more fresh groceries, Groceries account for ¼ of $ Store sales. Both Channels generally offer most of the same product categories, but the actual product mix is different.